 |
| |
| Get the benefits
of a structured and cross-disciplinary curriculum delivered in
our web solutions. Developed by math educators and experts, our curriculum
integrates the best of both Eastern and Western approaches.
It not only prepares your child for school, but also for the
world outside the classroom. |
| |
|
| |
|
The development of our networked curriculum begins with a
careful analysis of the foundational knowledge required for
each topic. In scrutinizing each topic's material, we are
able to identify its pre-requisite topics the building blocks
a child must complete before approaching this topic.
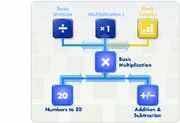 For
example, before a child learns basic multiplication, he or
she needs to have a good foundation in numbers and addition.
These will help him or her grasp the underlying concept of multiplication,
which is grouping objects together. Then, after a student
gains proficiency in basic multiplication, it becomes a foundation
block for other topics that require understanding of basic
multiplication, such as division (where groups are broken
down) and block graphs (where groups of numbers are represented
pictorially). For
example, before a child learns basic multiplication, he or
she needs to have a good foundation in numbers and addition.
These will help him or her grasp the underlying concept of multiplication,
which is grouping objects together. Then, after a student
gains proficiency in basic multiplication, it becomes a foundation
block for other topics that require understanding of basic
multiplication, such as division (where groups are broken
down) and block graphs (where groups of numbers are represented
pictorially).
|
|
|
|
 |
| |

Numbers to 10 |
 |
Counting, Reading, and Writing |
 |
Counting on and Counting back |
 |
Even and Odd Numbers |
 |
Comparing 2 Groups of Objects with 1-to-1 Correspondence |
 |
Composition of Numbers 1-10 |
|

Numbers to 20 |
 |
Counting, Reading, and Writing |
 |
Ordinal Numbers and Cardinal Numbers |
 |
Composition of Numbers 11-18 |
|

Basic Addition and
Substraction |
 |
Concept of Addition and Subtraction |
 |
Record Addition and Subtraction within 18 Horizontally |
 |
Understand Concept of Zero through Subtraction |
 |
Relationship between Addition and Subtraction |
 |
Commutative Property of Addition through Concrete
Examples |
|

Numbers to 100 |
 |
Counting, Reading, and Writing |
 |
Recognition of the Units and Tens Places |
 |
Count in Groups of Two, Five, and Ten |
 |
Composition of Numbers 1 to 100 |
|

Addition and Substraction
I |
 |
Addition within 2 Places, Including
Carrying |
 |
Column Form of Calculation |
 |
Addition of Three Numbers |
 |
Subtraction within 2 Places, Excluding Decomposition |
 |
Solve Simple Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Length and Distance
I |
 |
Length and Distance |
 |
Compare Lengths of Objects and Distances between
Objects Directly |
 |
Compare Lengths of Objects and Distances between
Objects with Improvised Units |
 |
Measure with Appropriate Improvised Units |
|

Money I |
 |
Identify the Coins of Money |
 |
Read Price Tags |
 |
Practice Using Coins through Activities |
 |
Solve Simple Problems |
|

Length and Distance
II |
 |
Understand the Need for Using Standard
Unit |
 |
Introduce Centimeter (cm) |
 |
Measure and Compare Lengths of Objects and Distances
Between Objects with cm |
 |
Estimate the Lengths of Objects with "Ever-Ready
Rulers" |
 |
Measure with Appropriate Tools |
|

Time I |
 |
Introduce "Hour" |
 |
Tell Time in Terms of O'clock |
 |
Introduce Days of a Week |
 |
Recognize there are 12 Months in a Year |
 |
Read out Dates and Days from a Calendar |
|

3-D Shapes I |
 |
Compare the Attributes of 3-D Objects |
 |
Recognize 3-D Shapes Intuitively |
 |
Group 3-D Shapes into Prisms, Pyramids, and
Spheres |
|

Straight Lines and
Curves |
 |
Recognize Straight Lines and Curves |
 |
Identify Straight Lines and Curves Intuitively |
 |
Make Straight Lines and Curves in a Variety
of Ways |
|

2-D Shapes |
 |
Identify Triangles, Quadrilaterals,
Pentagons, Hexagons, and Circles |
 |
Identify 2-D Shapes Intuitively |
 |
Identify Squares and Rectangles Intuitively |
 |
Make 2-D Shapes in a Variety of Ways |
|
|
 |
| |
|
 |
|

3-Digit Numbers |
 |
Counting, Reading, and Writing |
 |
Recognize Place Value "Hundreds" |
 |
Count in Groups of Fifty or Hundred |
 |
Estimate the Quantity of Objects |
|

Addition and Substraction
II |
 |
Perform Addition within 3 Places,
incl. Carrying, and Addition of 3 Numbers |
 |
Subtraction within 2 Places, Including Decomposition |
 |
Solve Simple Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Basic Multiplication |
 |
Develop Concept of Multiplication |
 |
Construct the Multiplication Tables (1-10) |
 |
Perform Basic Multiplication |
 |
Commutative Property of Multiplication through
Concrete Examples |
 |
Solve Simple Problems |
|

4-Digit Numbers |
 |
Counting, Reading, and Writing |
 |
Recognize the Place Value "Thousands" |
 |
Count in Groups of Five Hundred and Thousand |
|

Addition and Substraction
III |
 |
Subtraction within 3 Places, Including
Decomposition |
 |
Associative Property of Addition through Concrete
Examples |
 |
Mixed Operations of Addition and Subtraction
(at most 2 operations) |
 |
Solve Simple Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|
Basic Division |
 |
Develop Concept of Division |
 |
Sums for Division, Including Sums with Remainders |
 |
Relationship between Multiplication and Division |
 |
Length and Distance |
|

Length and Distance
III |
 |
Understand the Need for Using a
Larger Unit for Measuring |
 |
Introduce "Meter" (m) |
 |
Measure and Compare Lengths of Objects and Distances
Between Objects with m |
 |
Measure with Appropriate Measuring Tools |
 |
Record the Lengths of Objects with Appropriate
Measuring Units |
 |
Estimate the Lengths of Objects with "Ever-Ready
Rulers" |
|

Time II |
 |
Introduce "Minute" |
 |
Tell Time in Terms of O'clock and Minutes |
 |
Measure the Duration of Time Spent on Different
Activities Using "Hours" and "Minutes" |
 |
Report the Duration of Time Spent on Different
Activities Using "Hours" and "Minutes" |
 |
Recognize that there are 24 Hours in a Day |
 |
Develop the Concept of "Morning" and "Afternoon" |
 |
Tell Time in Terms of "Morning," "Afternoon,"
"Noon" and "Midnight" |
 |
Recognize the Number of Days in Each Month |
 |
Recognize the Number of Days in a Year and Leap
Year |
|

Money II |
 |
Identify Notes and Coins |
 |
Read Price Tags |
 |
Exchange Current Notes and Coins |
 |
Solve Simple Problems--Addition and Subtraction
of Money |
|

Weight |
 |
Develop the Concept of Weight |
 |
Compare the Weights of Objects Directly |
 |
Measure and Compare the Weights of Objects Using
Improvised Units |
 |
Understand the Need for Using Standard Units |
 |
Measure and Compare the Weights of Objects Using
"Gram" and "Kilogram" |
 |
Choose the Appropriate Tools for Measuring |
 |
Record the Weights of Objects with Suitable
Units |
|

3-D Shapes II |
 |
Identify Prisms and Cylinders Intuitively |
 |
Identify Pyramids and Cones |
 |
Recognize Faces Intuitively |
 |
Group 3-D Shapes |
 |
Make 3-D Shapes |
|

Angles I |
 |
Introduce Angles |
 |
Introduce Right Angles |
 |
Compare the Sizes of Angles |
 |
Make Angles in a Variety of Ways |
|

The Four Compass Points
|
 |
Recognize the Four Directions:
North, East, South and West |
 |
Use a Compass to Measure Directions |
|

Quadrilaterals I |
 |
Develop the Concept of Quadrilaterals |
 |
Recognize and Identify Quadrilaterals |
 |
Construct Quadrilaterals in a Variety of Ways |
|
Pictograms I |
 |
Compare Quantity of 3 or More Types
of Objects by Arranging them in Lines |
 |
Read and Discuss Simple Pictograms |
 |
Construct Pictograms, Using a One-to-One Representation |
|
|
 |
| |
|
 |
| |

5-Digit Numbers |
 |
Counting, Reading, and Writing |
 |
Recognize the Place Value "Ten Thousands" |
 |
Solve Simple Problems |
|

Addition and Substraction
IV |
 |
Perform Addition and Subtraction
Within Four Places |
 |
Apply the Commutative and Associative Properties
of Addition in Computation |
 |
Solve Simple Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Multiplication I |
 |
Perform Multiplication with Multiplier
1 Digit and Multiplicand 2 Digits |
 |
Perform Multiplication with Multiplier 1 Digit
and Multiplicand 3 Digits |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Division I |
 |
Perform Basic Division by Short
Division |
 |
Perform Division with Divisor 1 Digit and Dividend
2 Digits |
 |
Perform Division with Divisor 1 Digit and Dividend
3 Digits |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Mixed Operations I |
 |
Recognize and Use Parentheses in
Mixed Operations |
 |
Perform Mixed Operations of: 1) Multiplication
and Addition; 2) Multiplication and Subtraction
(For Sums Involving at Most 2 Operations) |
 |
Solve Problems Involving Addition and Subtraction,
Multiplication and Addition, and Multiplication
and Subtraction |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Fractions I |
 |
Develop the Concept of Fractions
as Part of One Whole and a Part of a Set of Objects |
 |
Recognize the Relationship between Fractions
and 1 |
 |
Compare Fractions with Same Denominator or Numerator |
 |
Solve Simple Word Problems |
|

Length and Distance
IV |
 |
Understand the Need for Using a
Unit Greater than "Meter" for Measurement |
 |
Introduce "Kilometer" |
 |
Compare Lengths of Objects and Distances between
Objects Using "Kilometer" |
 |
Understand the Necessity of Using a Unit Smaller
than "Centimeter" for Measurement |
 |
Introduce "Millimeter" |
 |
Compare Lengths of Objects and Distances between
Objects Using "Millimeter" |
 |
Choose the Appropriate Tools for Measuring |
 |
Record Lengths of Objects and Distances Between
Objects with Appropriate Units |
 |
Solve Simple Problems |
|

Time III |
 |
Introduce "Second" |
 |
Tell Time |
 |
Record the Duration of Time for Different Activities
Using "Second" |
 |
Record the Duration of Time for Different Activities
Using "Hour and Minute" or "Minute and Second" |
|

Capacity |
 |
Develop the Concept of Capacity |
 |
Compare the Capacity of Containers Directly |
 |
Measure and Compare the Capacity of Containers
Using Improvised Units |
 |
Understand the Need for Using Standard Units |
 |
Measure and Compare the Capacity of Containers
Using "Liter" and "Milliliter" |
 |
Measure with Appropriate Tools |
 |
Record the Capacity of Containers with Appropriate
Units |
|

Time IV |
 |
Introduce the "24-Hour Time" |
 |
Tell Time from 24-Hour Clocks |
 |
Recognize the Use of "24-Hour Time" in Daily
Life Situations |
|

Parallel and Perpendicular
Lines |
 |
Recognize Parallel Lines |
 |
Make Parallel Lines in a Variety of Ways |
 |
Recognize Perpendicular Lines |
 |
Make Perpendicular Lines in a Variety of Ways |
|

Quadrilaterals II |
 |
Develop an Understanding of the
Characteristics of Squares and Rectangles |
 |
Develop an Understanding of the Characteristics
of Parallelograms |
 |
Compare the Characteristics of Squares, Rectangles,
and Parallelograms |
|

Angles II |
 |
Recognize Acute Angles and Obtuse
Angles |
 |
Compare the Sizes of Angles |
|

Triangles |
 |
Recognize the Simple Characteristics
of Triangles |
 |
Recognize Some Special Triangles, such as Right-Angled
Triangles, Isosceles Triangles, Equilateral Triangles
and Scalene Triangles |
 |
Make Triangles |
|
Block Graphs |
 |
Read and Discuss Block Graphs |
 |
Construct Block Graphs: 1) Collect Data and
Construct Freq. Tables; 2) Construct Graphs Using
a One-to-One Representation; 3) Discuss the Block
Graphs Constructed |
 |
Estimate the Average from Block Graphs |
|
Bar Charts I |
 |
Read and Discuss Simple Bar Charts,
and Introduce the Vertical and Horizontal Axes |
 |
Construct Simple Bar Charts: 1) Use 1-to-1 Representation;
2) Use 2-to-2, 1-to-5, or 1-to-10 Representation;
3) Discuss the Bar Charts Constructed |
 |
Estimate the Average from Bar Charts |
|
|
 |
| |
|
 |
| |

Multiplication II |
 |
Discover the Associative Property
of Multiplication through Concrete Examples e.g.,
(3x2) x 5 = 3 x (2x5) |
 |
Apply the Commutative and Associative Properties
of Multiplication in Computation e.g., 2x8x5 =
(2x5) x 8 |
 |
Perform Multiplication with Multiplier 2 Digits
and Multiplicand 2 Digits |
 |
Perform Multiplication with Multiplier 2 Digits
and Multiplicand 3 Digits |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Division II |
 |
Perform Division with Divisor 2
Digits and Dividend 2 Digits |
 |
Perform Division with Divisor 2 Digits and Dividend
3 Digits |
 |
Recognize Divisibility, Divisibility Tests for
2, 5 and 10 |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Calculators |
 |
Be Familiar with Modern Calculating
Devices |
 |
Recognize the Basic Operations and Functions
of a Calculator |
 |
Use Calculators to Carry Out Activities to Foster
Pupil's Number Sense |
|

Multiples and Factors
|
 |
Develop an Understanding of Multiples |
 |
Develop an Understanding of Factors |
 |
Find Out All the Factors of a Number |
 |
Explore the Relationship between Factors and
Multiples |
 |
Introduce Prime and Composite Numbers |
|

Common Multiples and
Common Factors |
 |
Develop an Understanding of Common
Multiples |
 |
List the Multiples of Two Numbers, Hence Find
the Common Multiples and the Least Common Multiple
of the Two Numbers |
 |
Develop an Understanding of Common Factors |
 |
List the Factors of Two Numbers, Hence Find
the Common Factors and the Highest Common Factor
of the Two Numbers |
 |
Find the Highest Common Factors of Two Numbers
by Short Division |
|
Mixed Operations II |
 |
Perform Mixed Operations of: 1)
Division and Addition; 2) Division and Subtraction;
3) Division and Multiplication (For Sums Involving
at Most 2 Operations) |
 |
Perform Mixed Operations for Sums involving
at most Four Steps |
 |
Introduce the Distributive Property of Multiplication
|
 |
Solve Problems involving Mixed Operations |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Fractions II |
 |
Develop the Concept of Proper Fractions,
Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers |
 |
Reduce Fractions to their Simplest Form |
 |
Explore the Methods for Converting Equivalent
Fractions |
 |
Find Common Denominators to Compare Fractions |
 |
Add and Subtract Fractions with the Same Denominators
and Reduce the Answers to the Simplest Form |
|

Decimals I |
 |
Recognize Decimals as Another Way
of Recording Fractions |
 |
Develop the Concept of Place Value in Decimals |
 |
Recognize the Use of Decimals in Daily Life
Situations |
 |
Perform the Addition and Subtraction of Decimals
up to Two Places of Decimals and for Sums Involving
at most Three Operations |
 |
Solve Problems involving Money, Length, and
Distance |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|
Perimeter I |
 |
Develop the Concept of Perimeter |
 |
Measure the Perimeter of 2-D Shapes |
 |
Find the Perimeter of Squares and Rectangles |
 |
Find the Perimeter of Simple 2-D Shapes |
|

Area I |
 |
Develop the Concept of Area |
 |
Direct Comparison of the Area of Surfaces |
 |
Compare the Area of Surfaces Using Improvised
Units |
 |
Introduce the Standard Units Square Centimeter
and Square Meter |
 |
Measure the Area of 2-D Shapes Using Square
Centimeters and Square Meters |
 |
Understand and Apply the Formulas for Calculating
the Area of Squares and Rectangles |
|

Quadrilaterals III |
 |
Develop an Understanding of the
Characteristics of Trapezoids and Rhombuses |
 |
Compare the Characteristics of Different Types
of Quadrilaterals |
 |
Find the Perimeter of Simple 2-D Shapes |
|

Fitting and Dissecting
Shapes |
 |
Make shapes by Fitting 2-D Shapes
Together |
 |
Dissect Polygons and Identify the Shapes Dissected |
|

Simple Symmetry |
 |
Develop an Understanding of Symmetrical
Shapes, and Find the Line(s) of Symmetry |
 |
Make Symmetrical Shapes |
|

Pictograms II |
 |
Read and Discuss Pictograms |
 |
Construct Pictograms of Greater Frequency Counts:
1) Organize and Classify Data Appropriately; 2)
Round Off Data to the Nearest Unit; 3) Construct
Pictograms, Using a One-to-Ten or a One-to-Hundred
Representation |
 |
Discuss the Pictograms Constructed |
|
|
 |
| |
|
 |
| |

Large and Negative
Numbers |
 |
Counting, Reading, and Writing |
 |
Rounding off Large Numbers Using Examples from
Everyday Life |
 |
Introduce Terms Natural Number and Integer |
 |
Introduce Negative Numbers and Compare with
Other Numbers |
 |
Estimation of Large Quantities |
|
Fractions III |
 |
Multiply Fractions through Repeated
Addition |
 |
Division of Fractions through Dissection of
Shapes |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Decimals II |
 |
Develop an Understanding of Multiplication
of Decimals, Multipliers Include Whole Numbers
Only |
 |
Develop an Understanding of Division of Decimals,
Including a Decimal Divided by a Whole Number
and a Whole Number Divided by a Whole Number |
 |
Find the Approximate Values by Rounding off
the Answers |
 |
Perform Mixed Operations on Decimals for Sums
Involving at Most Three Operations |
 |
Solve Problems involving Money, Length, and
Distance |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Fractions IV |
 |
Perform Multiplication of Fractions,
for Sums Involving at Most Two Operations |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Decimals III |
 |
Convert Decimals into Fractions |
 |
Convert Fractions into Decimals, Rounding off
the Answers to the Nearest Tenths or Hundredths |
 |
Compare Fractions by Converting Them into Decimals |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Percentages I |
 |
Recognize the Use of Percentages
in Daily Life |
 |
Length and Distance |
 |
Convert Percentages into Decimals and Vice Versa |
 |
Convert Percentages into Fractions and Vice
Versa |
|
Area II |
 |
Understand and Apply the Formulas
for Calculating the Area of Parallelograms, Triangles
and Trapezoids |
 |
Find the Area of Polygons |
|

Temperature |
 |
Develop the Concept of Temperature |
 |
Introduce "Celsius" and "Fahrenheit" |
 |
Read Temperature using Appropriate Tools |
 |
Use Temperature in Real-Life Examples |
 |
Convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Volume I |
 |
Develop the Concept of Volume |
 |
Compare the Volume of Objects Intuitively |
 |
Introduce the Standard Unit "Cubic Centimeter" |
 |
Measure and Compare the Volume of Objects Using
"Cubic Centimeter" |
 |
Understand the Need for Using a Unit Larger
than "Cubic Centimeter" |
 |
Introduce "Cubic Meter" |
 |
Understand and Apply the Formulas for Finding
the Volume of Cubes and Cuboids |
|

Other Counting Systems
|
 |
Introduce the British System: Distance,
Capacity, Weight |
 |
Measure Objects using British Units and Compare
them Intuitively |
 |
Introduce, Convert, and Use Roman Numerals |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

The Eight Compass Points |
 |
Recognize the Eight Compass Points |
 |
Find Directions with a Compass |
|

3-D Shapes III |
 |
Recognize the Characteristics of
Cones, Pyramids, Cylinders, Prisms and Spheres |
 |
Make Nets of Cubes and Cuboids |
|

Angles III |
 |
Introduce "degree" |
 |
Identify proper angles (30, 45, 60, 90, 180,
360) |
 |
Identify and measure angles in 2-D shapes |
 |
Measure angles using appropriate tools |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Bar Charts II |
 |
Read and Discuss Bar Charts |
 |
Identify proper angles (30, 45, 60, 90, 180,
360) |
 |
Read and Discuss Compound Bar Charts |
 |
Construct Compound Bar Charts and Discuss the
Bar Charts Constructed |
|

Simple Statistics |
 |
Introduce Quartile Regions, Average,
Range, Mean, Median, and Mode |
 |
Solve Simple Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Bar Charts III |
 |
Read and Discuss Bar Charts of
Large Frequency Amounts |
 |
Construct Bar Charts: 1) Using a 1-to-10,000
or a 1-to-100,000 Representation |
 |
Estimate the Average from Bar Graphs |
|

Elementary Algebra |
 |
Use Symbols or Letters to Represent
Numbers |
 |
Record with Algebraic Symbols (e.g., John is
x years old now, how old will he be after 10 years?
Record as: (x+10) Years Old |
|

Simple Equations I
|
 |
Understand the Concept of Equations |
 |
Solve Simple Equations Involving One Step in
the Solutions, and Check the Answers (Involving
Whole Numbers Only) |
 |
Rewrite Equations into Equivalent or Simplified
Expressions |
 |
Solve Problems by Simple Equations, Involving
at Most One Step in the Solutions |
|
|
 |
| |
|
 |
| |

FractionsV |
 |
Perform Division of Fractions for
Sums Involving at Most Two Operations |
 |
Solve Simple Problems, Excluding Problems on
Finding the Original Numbers |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Decimals IV |
 |
Multiply Decimals by Decimals |
 |
Divide Decimals by Decimals |
 |
Introduce Recurring Decimals |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Percentages II |
 |
Solve Simple Problems on Percentages,
Including: 1) Find Percentages; 2) Express the
Value of a Percentage of a Quantity; 3) Discount |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Volume II |
 |
Recognize the Relationship between
Capacity and Volume |
 |
Find the Volume of Irregular Solids by Displacement
of Water |
|

Perimeter II |
 |
Develop an Understanding of Circumference |
 |
Explore the Relationship between the Circumference,
the Diameter and the Radius |
 |
Develop an Understanding of pi |
 |
Apply the Formula for Circumference |
|

Speed |
 |
Develop the Concept of Speed |
 |
Measure Speed Using "Meters per Second" and
"Kilometers per Second" as Units |
 |
Read Travel Graphs |
|
Area III |
 |
Understand and Apply the Formula
for Calculating the Area of a Circle |
 |
Relationship between Circumference and Area
of a Circle |
 |
Length and Distance |
|

Symmetry II |
 |
Introduce Transformations (Scale,
Translation, Reflection, Rotation) |
 |
Introduce Congruence and Similarity |
 |
Perform Transformations Showing that Two Shapes
are Congruent or Similar |
 |
Identify the Line of Rotational Symmetry in
3-D Figures |
 |
Solve Problems |
|

3-D Shapes IV |
 |
Recognize the Vertices, Edges and
Faces of 3-D Shapes |
 |
Make Frameworks of Prisms and Pyramids |
 |
Explore the Relationship between the Number
of Edges and the Number of Sides of the Bases
of Prisms and Pyramids |
 |
Explore the Relationship between the Number
of Vertices and the Number of Sides of the Bases
of Prisms and Pyramids |
 |
Explore and Design Nets of Prisms |
 |
Make Pyramids and Prisms |
 |
Recognize the Different Sections of Prisms,
Pyramids and Spheres |
|

Circles |
 |
Develop an Understanding of the
Properties of Circles, Center, Radius, Diameter
and Circumference |
 |
Draw Circles in a Variety of Ways |
|

Broken Line Graphs |
 |
Read and Discuss Broken Line Graphs |
 |
Construct Broken Line Graphs |
|

Simple Probability |
 |
Acquire an Elementary Understanding
of Probability |
 |
Justify Conclusions involving "and/or" Situations |
 |
Describe the Probability of Events Happening
Using the Following Phrases: 1) Likely / Probable;
2) Unlikely / Not Probable; 3) Fairly Likely;
4) Very Probable; 5) Certain |
|

Ratio and Proportion
|
 |
Introduce Inverse and Direct Proportions |
 |
Introduce Ratios |
 |
Solve Problems |
 |
Estimate the Answers |
|

Simple Coordinate Geometry |
 |
Introduce the Rectangular Coordinate
System |
 |
Use the Coordinate Plane to Explore Geometric
Ideas |
 |
Make and Use Coordinate Geometry to Specify
Locations and to Describe Paths |
 |
Solve Problems |
|

Pie Charts |
 |
Reading Pie Charts |
 |
Making Pie Charts using Compass and Protractor |
|

Simple Equations II |
 |
Solve Equations Involving at Most
Two Steps in the Solutions, and Examine the Results |
 |
Solve Simple Problems By Equations, Involving
at Most Two Steps in the Solutions |
|
|
 |
| |
|
|
|
 Curriculum
Details Curriculum
Details |
|
|
 |
|


 For
example, before a child learns basic multiplication, he or
she needs to have a good foundation in numbers and addition.
These will help him or her grasp the underlying concept of multiplication,
which is grouping objects together. Then, after a student
gains proficiency in basic multiplication, it becomes a foundation
block for other topics that require understanding of basic
multiplication, such as division (where groups are broken
down) and block graphs (where groups of numbers are represented
pictorially).
For
example, before a child learns basic multiplication, he or
she needs to have a good foundation in numbers and addition.
These will help him or her grasp the underlying concept of multiplication,
which is grouping objects together. Then, after a student
gains proficiency in basic multiplication, it becomes a foundation
block for other topics that require understanding of basic
multiplication, such as division (where groups are broken
down) and block graphs (where groups of numbers are represented
pictorially).